Tiny Storm SQL: A Real Time Stream Data Analysis Interface for Apache Storm
SQL is a well-adopted interface especially for those non-computer major people. Several projects including Hive, Drill, Phoenix and Spark have already invested significantly in their SQL layers. Here we implement a Storm-based query language system for real time stream data analysis.
Relevant Research
For Apache storm 1.1.0 or later version, it has already provided Streaming SQL. In VLDB-2016, EPFL DATA Lab implemented a streaming online query processing / analytics engine based on Apache Storm named squall.
System Architecture
Here we just implement a similar demo system which supports real time stream data analysis. The whole architecture is shown below:
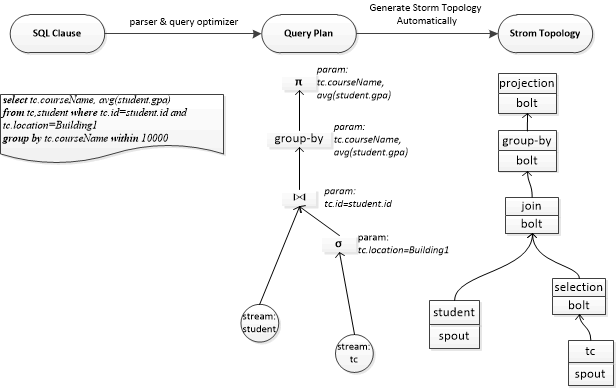
As we can see from the above picture, when the user type a SQL-formatted query clause, the query sequence will be translated into a query plan which presents in the shape of a directed acyclic graph. The DAG-formatted query plan is optimized. Then it will be mapped into a Storm topology dynamically. Then the topology will be submitted to Storm cluster for running.
Key Compoments
Here, the SQL parser is implemented by taking use of ANTLR. ANTLR(ANother Tool for Language Recognition) is a powerful parser generator. Here we design the following BNF-formatted grammar for SQL:
grammar sql; @header { package storm_sql.parser; } root : 'select' select_list 'from' table_sources ('where' search_condition)? ('group' 'by' group_by_item (',' group_by_item)*)? ('having' search_condition)? ('within' within_time)? ; select_list : select_list_elem (',' select_list_elem)* #printSelectList ; select_list_elem : /*(table_name=ID '.' column_name=ID)*/ expression #printSelectListElem | aggregate_function'(' expression ')' #selectAggregateFunction ; ID : [a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z_0-9]* ; table_sources : table_source (',' table_source)* #tableSources ; table_source : ID #tableSource ; expression : aggregate_function #exprAggrFunc | (table_name '.' column_name) #expr | NUM #num | ID #id ; NUM : '-'[1-9][0-9]* | '0' | [1-9][0-9]* ; table_name : ID #tableName ; column_name : ID #columnName ; aggregate_function : 'avg' | 'max' | 'min' | 'sum'| 'count' ; search_condition : search_condition_and ('and' search_condition_and)* #printSearchCondition ; search_condition_and : expression comparison_operator expression #printSearchConditionAnd //| '(' search_condition ')' ; comparison_operator : '=' | '>' | '<' | '<=' | '>=' | '!=' ; group_by_item : expression #groupByItem ; within_time : (NUM) #withinTime ; WS : [ \t\r\n]+ -> skip ; // Define whitespace rule, toss it out
By ANTLR -visitor tool, we can easily visit the AST through visitor design pattern. We store the necessary info of the sql sequence to build the DAG-formatted query plan. Here we use JGraphT to traverse the DAG, since it provides various interfaces for handling the DAG. We can eliminate the trouble of reinventing the wheel.
To automatically generate Storm topology from the DAG-formatted query plan, we need to mark the father and child of each node in the DAG. In the DAG, the source tables are Storm spouts in Storm topology. Similarly, the operators of the DAG is storm bolts in Storm topology, so you need to implement these bolts ahead of schedule. Notice, join and group-by operators are time window based, in Storm, you can simply extend BaseWindowedBolt to implement the concepts of time window. Of course, you also have to connect to data sources to create Storm spouts to get the stream data. Here we simply create two spouts named student and tc to simulate the stream source data.
The key features of the system include:
-
the SQL parser is based on
ANTLR, it is universal for users' typing input; -
the DAG-formatted query plan is based on
JGraphT, you can access any vertex as you want; -
the Storm topology is generated from the query plan
dynamically, that is to say the whole system is not limited to a specific application or a specific stream data.
Of course, the demo system is nothing but a demo, there is a lot to be improved. However, you can follow the whole architecture to develop your own interface.
For more details about the src, see here...
Any questions or suggestions, feel free to open an issue @here or e-mail me to lijiansong@ict.ac.cn.